Describe the Gross and Microscopic Structure of the Spinal Cord
N The spinal cord is roughly cylindrical in shape. First week only 499.
Caudal to this a terminal.
. Describe the gross and microscopic structure of the spinal cord. Spinal Cord I Gross and Microscopic Structures study guide by oliviasullivan89 includes 32 questions covering vocabulary terms and more. Describe the gross and microscopic structure of the spinal cord.
Start your trial now. Explain how information passes from one neuron to another. Perperdicular to the longitudinal axis of the nervous system side to side and top to bottom -in brain vertical to the ground.
Provides a 2 way conduction path. Arrow parallel to the longitudinal axis and is the midline of the nervous system. Name the parts of a reflex arc and describe the function of each part.
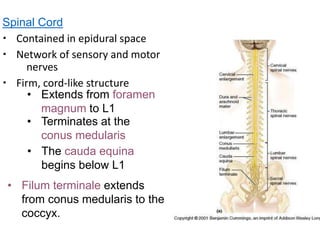
The spinal cord is a part of the central nervous system. The spinal cord is a single structure whereas the adult brain is described in terms of four major regions. N It terminates inferiorly in the adult at the level of the lower border of the L1.
Describe the gross and microscopic structure of the spinal cord. It is a long pipe-like structure arising from the medulla oblongata part of the brain consisting of a collection of nerve fibres running through the vertebral column of the backbone. The Spinal Cord Expected Learning Outcomes State the three principal functions of the spinal cord.
Trace the pathways followed by nerve signals traveling up and down the spiral cord. The cerebrum the diencephalon the. Quizlet flashcards activities and games help you improve your grades.
They involve the brain spinal cord and peripheral nerves. The spinal cord is a cylinder of CNS. The region of spinal cord caudal to the lumbar enlargement is conus medullaris.
Describe the coverings of the brain and spinal cord. Examine and describe the gross and microscopic anatomy of the spinal cord spinal ganglia spinal nerves and spinal meninges. Surface Anatomy Spinal cordcylinder of nervous tissue that arises from the brainstem at the foramen magnum of the skull Occupies the upper two-thirds of vertebral canal Inferior margin ends at L1 or slightly beyond Averages 18 cm thick and.
Solution for Describe the gross and microscopic structure of the spinal cord. Each segment of the spinal cord provides several pairs of spinal nerves which exit from vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramina. It is covered by the three membranes of the CNS ie the dura mater arachnoid and the innermost pia mater.
Name the major parts and functions of the brain. Spinal cord enclosed in the vertebral column extends from the foramen magnum of the skull to the level of the first or second lumbar vertebra just inferior to the ribs. Provides a 2 way conduction path to and from the brain.
The spinal cord is a long white cord located in the vertebral canal transfers nerve impulse to 31 pairs of spinal nerves communicating the brain with the body with two basic functions. The pia along with the arachnoid are referred to as the leptomeninges whereas the dura is. -midsagittal seciton divides the brain into two hemispheres.
Gross anatomy of the spinal cord. It is continuous to the level of the second lumbar vertebra. Like the vertebral column the spinal cord is divided into segments.
Describe the gross and microscopic structure of the spinal cord. Spinal cord enclosed in the vertebral column extends from the foramen magnum of the skull to the level of the first or second lumbar vertebra just inferior to the ribs. Cervical thoracic lumbar sacral and coccygeal.
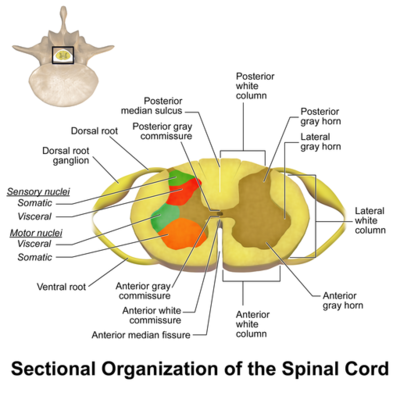
The epineurium or outer layer consists of a dense network of collagen fibers. -in spinal cord horizontal to the ground. It is segmented with a pair of roots dorsal and ventral roots consisting of nerve fibres joining to form the spinal nerves.
Gross Anatomy The spinal cordfig. The spinal cord extends from the medulla oblongata. It extends from the foramen magnum to the end of the first lumbar vertebra.
These plates expand dorsally and ventrally to produce the H-shaped central mass of gray matter of the adult spinal cord. The spinal cord a two-way impulse conduction pathway and a reflex center resides within the vertebral column and is protected by meninges and cerebro-spinal fluid. 131 is a cylinder of nervous tissue that begins at the foramen magnum and passes through the vertebral canal as far as the inferior margin of the first lum-bar vertebra L1.
External and Microscopic Anatomy of Human Spinal Cord. The spinal cord protected by the vertebral column begins at the occipital bone and extends down to the space between the first and second lumbar vertebrae. Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves issue from the.
N It begins superiorly at the foramen magnum in the skull. Every segment of the spinal cord is connected to a pair of spinal nerves each of which is surrounded by a series of 3 connective tissue layers that support structures and contain blood vessels. There are 8 pairs of cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 5 sacral and 1 coccygeal pair of spinal nerves a total.
N In the young child it usually ends at the upper border of L3. The pia arachnoid and the dura mater see the image below. Examine the microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue.
The meninges consist of 3 tissue layers that cover the brain and spinal cord. The spinal cord has a varying width ranging from 05 inch thick in the cervical and lumbar. The spinal cord exhibits subtle cervical and lumbar lumbosacral enlargements produced by extra neurons in segments that innervate limbs.
The perineurium or middle layer divides the nerve into compartments. Describe its gross and microscopic structure. Describe compare and contrast selected aspects of neurophysiology.
Afferent in which they are carried sensory sensations trunk neck and four members to the brain and the efferent. Its diameter varies at different levels being enlarged in the cervical and lumbar regions. Categorize the structures of the nervous system into central or peripheral divisions.
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system CNS which extends caudally andis protected by the bony structures of the vertebral column. In adults it averages about 18 cm thick and 45 cm long. Describe the events that lead to the conduction of a nerve impulse.
The brain and the spinal cord are the central nervous system and they represent the main organs of the nervous system. In an adult the spinal cord is from 42 to 45 centimeters long. Describe the gross and microscopic structure of the spinal.
Gross Anatomy 37183 Views.

Anatomy And Physiology I Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves

Diagram Of Spinal Root And Spinal Nerve Microscopic Anatomy As Of Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment